Example I
Here you can find two simple examples of plotting results for heterogeneous treatment effects, one by using matrices:
Example
Data set
/*
Let's take some artificial data to show examples of using the coefplot when looking
at heterogeneous treatment effects.
*/
use "example_coefplot.dta", clear
*** First steps: how to test for heterogeneous treatment effects? ***
// Imagine you would like to check for heterogeneous treatment effects on y1
reg y1 i.treat##i.female
// What's the total treatment effect for women?
lincom 1.treat+1.treat#1.female
// Same, but contains total effects for both men and women
contrast r.treat@i.female
// Note that contrast comes with the option "post" to put results in return list
*** Estimate all models & plot them ***
// Loop over all models
local n = 1
foreach outcome in y1 y2 y3 {
reg `outcome' i.treat##i.female
contrast r.treat@i.female, post
est sto e`n'
local n = `n'+1
}
// Simple coefplot
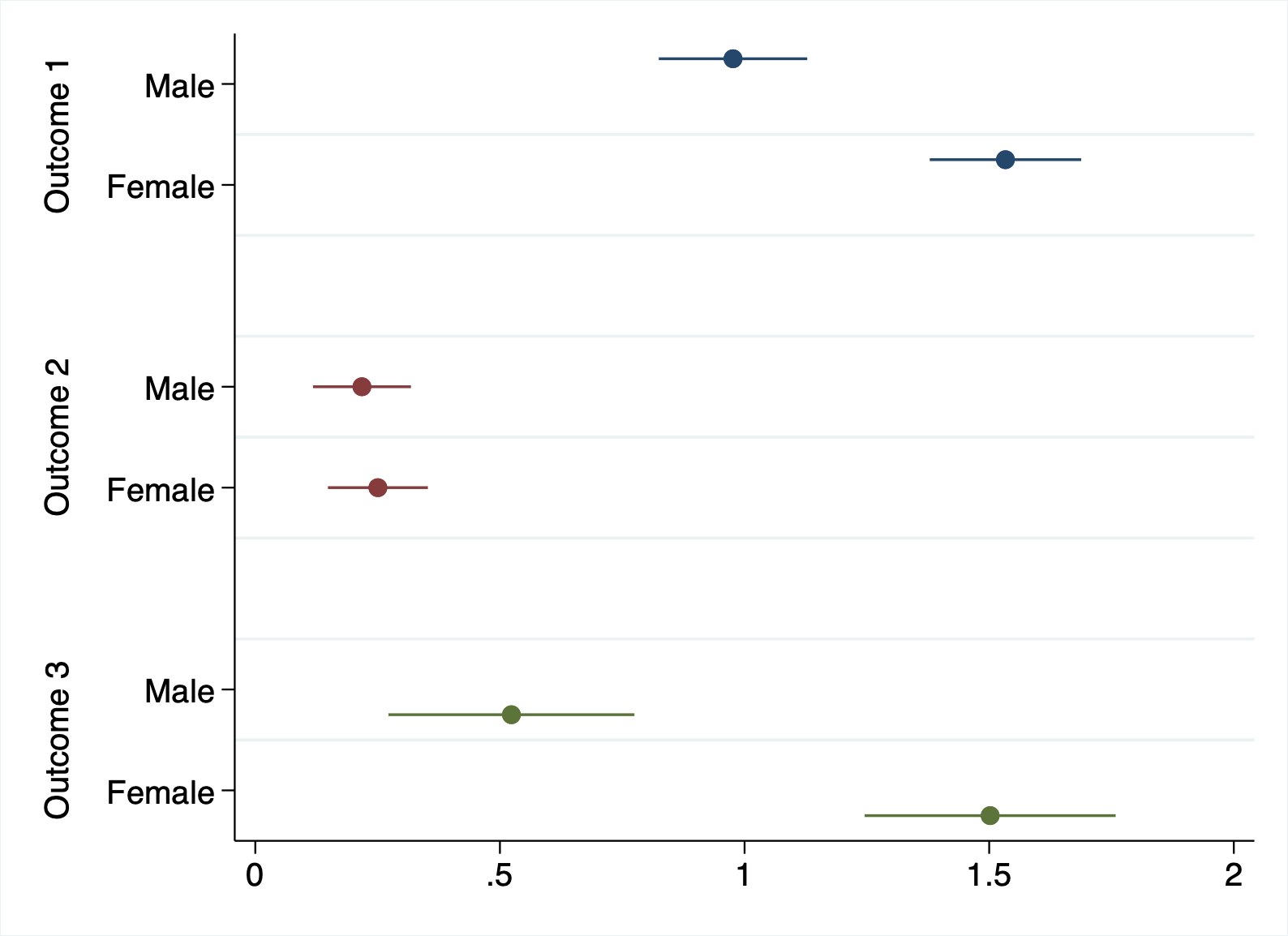
coefplot e1 e2 e3
// Let's do some refinements: use "aseq" and "eqstrict" to plot results by estimation
coefplot e1 e2 e3, ///
aseq eqstrict
// Some cosmetic changes
coefplot e1 e2 e3, ///
aseq eqstrict eqlab("Outcome 1" "Outcome 2" "Outcome 3") nokey ///
coeflab(*0.female="Male" *1.female="Female") ///
graphr(c(white))
*** More flexible (but also more complicated): Matrices ***
// Create empty matrices
mat A = J(3,3,.) // matrix to store treatment results for male
mat B = J(3,3,.) // matrix to store treatment results for female
// Same loop as before, now store results in matrix
local n = 1
foreach outcome in y1 y2 y3 {
reg `outcome' i.treat##i.female
mat A[`n',1] = r(table)[1,2] // coefficient of 1.treat
mat A[`n',2] = r(table)[5,2] // lower CI boundary of 1.treat
mat A[`n',3] = r(table)[6,2] // upper CI boundary of 1.treat
lincom 1.treat+1.treat#1.female
mat B[`n',1] = r(estimate) // coefficient of 1.treat+1.treat#1.female
mat B[`n',2] = r(lb) // lower CI boundary
mat B[`n',3] = r(ub) // upper CI boundary
local n = `n'+1
}
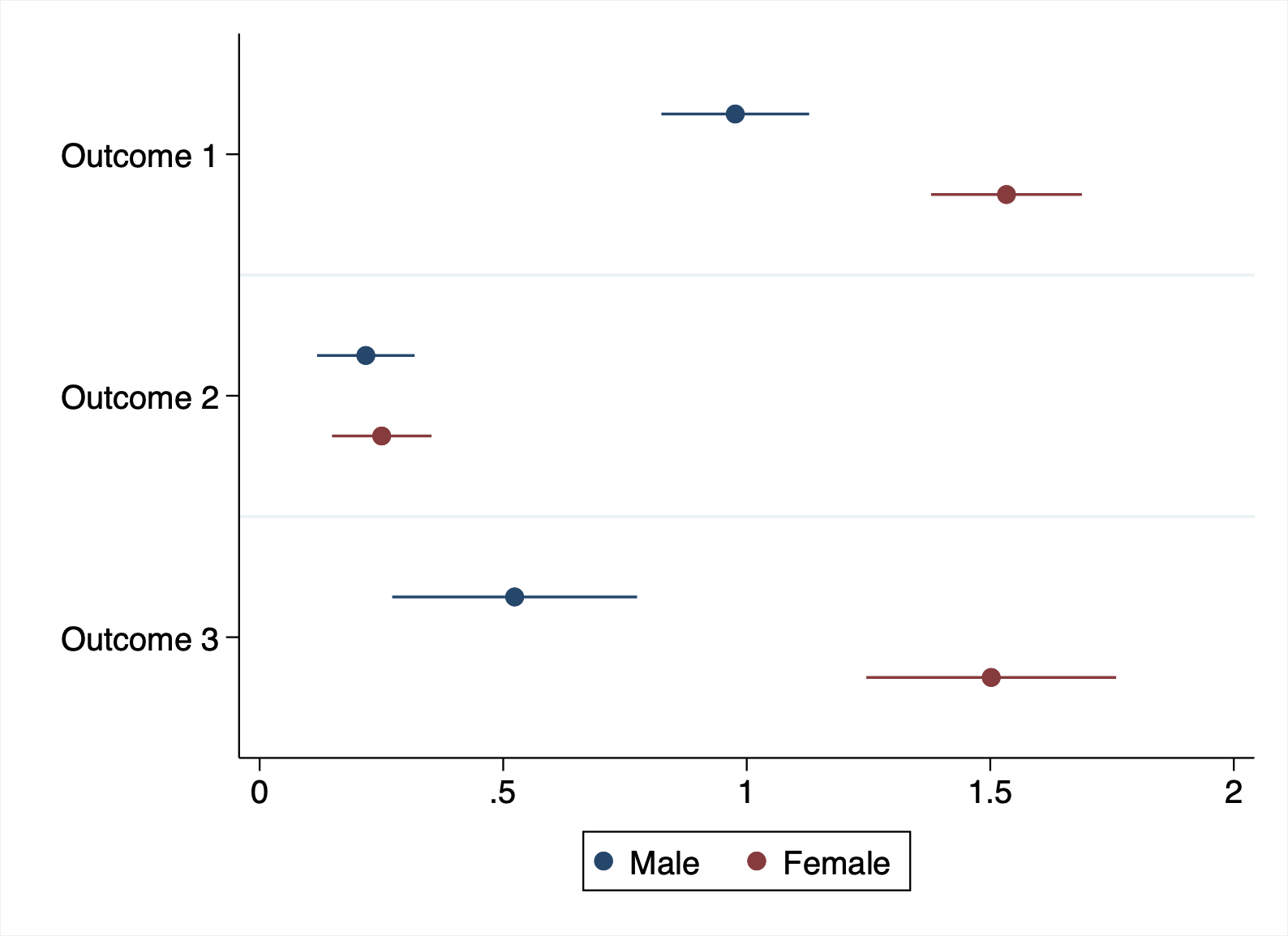
// Simple coefplot
coefplot (mat(A[.,1]), ci((2 3))) (mat(B[.,1]), ci((2 3)))
// Some refinements
coefplot (mat(A[.,1]), ci((2 3))) (mat(B[.,1]), ci((2 3))), ///
coeflab(r1="Outcome 1" r2="Outcome 2" r3="Outcome 3") ///
plotlab("Male" "Female") graphr(c(white))